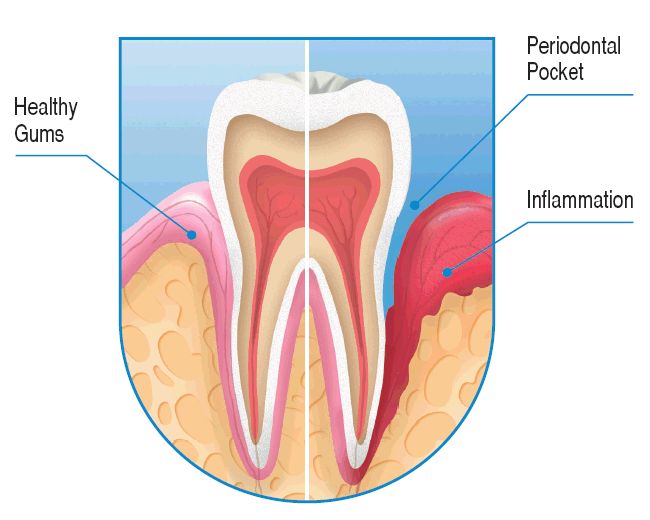
Periodontosis ili periodontal disease is a progressive and degenerative disease of the periodontium (supportive tooth tissue), leading to the loosening, migration and falling out of teeth. The main property of periodontal disease is the “naked” tooth neck and root caused by the decay of the connective tissue which fixes the tooth in the alveola (tooth bed) and consequential gum tissue withdrawal. Periodontal disease may be treated with conservative methods including a series of measures applied over a longer period of time, such as cleaning and treatment of periodontal pockets. Another treatment method is the surgical procedure aimed at establishing a good grip of the gums to tooth cementum, thus preventing further expansion of periodontal pockets. For this purpose, the most common procedures are flap surgery and gingivectomy. One modern method is laser treatment (photodynamic therapy) which involves the treatment of bacteria with a special fluid that is bound to bacterial membranes, while the light of the laser beam creates active oxygen which destroys them. The most common signs of periodontal disease are swollen and red gums, blood during brushing, gum tissue withdrawal. Periodontal disease is a condition which cannot be cured but only slowed down, so the most attention is paid to prevention, which includes regular visits to the dentist’s office.
